It is only with tongue firmly in cheek and a deep respect for the fact that I have enjoyed a relatively safe, comfortable, and very happy life that I state—cue swell of melodramatic music—the worst possible thing has happened:
My dishwasher died, mid-pandemic!

My dishwasher died, mid-pandemic!
This feels like a catastrophe because we run that appliance roughly four times most days with everyone working and/or learning remotely from home.
The Bosch dishwasher we got with this house no longer powers on following a few weeks of intermittent-but-increasing button-press failure. Our non-expert analysis of what was under the hood kick-plate didn’t reveal any obvious reset to try on our own. We have ordered a replacement.
For those who don’t already know me well, now is when I confess to being a thoroughly disinterested cook. The one time I directed a full kitchen remodel where my preferences reined over popular opinion, I bought almost literally the cheapest electric coil top! stove from Sears whilst splurging on a high end, German-made Miele dishwasher.
My priorities may not be common, but I’m quite clear on what they are.
The dishwasher is the most used appliance in our home excepting the stalwart, always-on refrigerator. It follows only central heating, running water, and refrigeration in my estimation of the crowning virtues of everyday technology.
Pandemic shortages & risks still affect appliance purchase, delivery & installation
Fortunately, more than half of our household of six is at least partially vaccinated, lessening the risk to us of having a plumber in to install a new machine. Risks to essential workers dealing with the public day in and day out remain much higher than those of their customers.
Since our atypical home includes a kitchen one story above ground level, we will also require delivery well inside the threshold. I imagine dishwasher delivery generally requires more than one single person. The model I chose weighs 107 lbs (48.5 kg.) That’s two more contacts outside our bubble.
Accomplishing this dishwasher replacement will mark the first time any tradesperson—let alone three outsiders—has entered our home since before the first shutdown began.
All of these health-preserving convolutions must also be viewed within the broader context of commerce in 2021. Plumbers were hard to book before COVID; getting one to show up now is beyond difficult.
Supply chains all over the world have been disrupted by the scourge of coronavirus infections. The Miele that I elected to replace my defunct Bosch SHU66C may have benefited in production from its maker’s domestic parts manufacturing, but getting the finished product from Germany to New England remains fraught with delays as of May 2021. The one I wanted due to arrive a few days after I contacted my favorite local appliance store is now back-ordered.
I’m not sure when I will get the new machine I’ve purchased, let alone how soon I can book professional installation by a qualified plumber.
I sought a short-term solution to maintaining household peace—and sanitation!—in the interim. A portable, countertop dishwasher is what I found.
Typical portable dishwasher requires standard faucets to accept adapter
I opted for an Aikoper Compact Portable Dishwasher with 6L Built-in Water Tank & Water Hose Inlet (Model KOP-DW2605A) ordered from Amazon.

There were a few “portable” dishwashers available locally, but all were variations on the design I know well from my first apartment: full- or almost-full-size models that roll up to the sink and connect with a special “quick connect” adapter that screws onto a standard faucet. These adapters replace an aerator (i.e., a little mesh screen that twists off easily) and are widely available in hardware stores and online.
The issue with any of those models is that we installed a modern “pull out sprayer” faucet when we moved here.
Pull out spray heads are great for everyday use. I like the option for one fewer hard-to-clean protrusion from the countertop, eliminating the off-to-the-side sprayer I grew up with
Or, as we did in this home, integrating the spray function into the faucet itself frees up that existing counter cut out for installation of a plumbed in, multi-stage water filter. I find the tap water in our community distinctly unpalatable without filtration beyond a carbon block pitcher.
Either way, I didn’t want to change my self-selected faucet to accommodate short-term daily use of the countertop dishwasher.
My purchase of the Aikoper Compact Portable was also influenced by the fact that we have historically hosted at least one very large Thanksgiving banquet each year. I see this little machine as a way to more quickly zip through the multi-day process of cleaning multitudes of party dishes at holidays in the future.
For both cases, I would have to ditch the faucet design I prefer to accommodate use of most portable dishwashers. There’s no way I’m going to swap out my faucet in either scenario.
Tank based, compact dishwasher alternatives exist & solve common issues
On Amazon,∞ I found a different portable dishwasher design.
Tank-based dishwashers like these seem to universally? include the option to connect via the adapter I’ve already described, yet they also incorporate a holding tank for the fresh, clean water that will be used to wash the dishes. A user can fill that tank via a pitcher or my preferred pull-out faucet, pouring water into the vented, screened hole on top after removing the loose-fitting white debris cap.
Once filled, tank-based machines complete their wash cycles without blocking access* to the kitchen sink throughout the run.
The included plastic pitcher and wide, flat funnel aren’t strictly necessary to manually fill the machine, but the funnel (marketed as the “pouring water assistant”) is particularly nice to have. 
Since the pitcher is marked to have a 1.8 L capacity, you might expect that filling it just over three times and emptying into your dishwasher tank might be sufficient to prepare the appliance rated as having 6 L capacity. It seemed to require at least five pitchers-full the first time I ran the machine to test its functionality.
Filling with a pull out faucet sprayer is much more convenient, especially for those of us who lack hand strength and become exhausted easily lifting full pitchers of water. I found it annoying to fill the appliance via a pitcher.
With the dishwasher sitting on a kitchen counter, it is a little bit high for me to reach over and fill, so I can’t see exactly where I’m aiming the water. The funnel helps channel every drop right into the receptacle where it belongs.
A 61 inch long water supply hose was included in the Aikoper box. The water supply hose has a right angle connection on one end which should help with keeping installation very close to a back wall. Remember that you will need a faucet adapter not included to install with this option.
If installing with the water supply hose option, your water pressure must be between 0.04 MPa and 1 MPa, per the Aikoper manual.
Because the water supply inlet and drain pipe outlet are set into an indented area at the back, bottom edge of the dishwasher and the supply hose has a right angle connection, the included hose should not require any additional clearance behind the appliance.
A side benefit of pre-filling the dishwasher with water, then letting it run without any connection to the household water supply, is that it eliminates that chilly scenario when a family member starts a built in model while someone else is showering.
In 2021, no one should live with plumbing that routinely scalds or runs cold, but that kind of annoyance remains common in many older homes.
Draining the used, dirty wastewater is also necessary. Tank-based dishwasher models like my Aikoper Compact Portable allow one to route the drainage hose into an adjacent sink or a large bucket.
The drain hose pictured was included in the Aikoper box. It’s about five feet long.
Because the water supply inlet and drain pipe outlet are set into an indented area at the back, bottom edge of the dishwasher but the drain hose has a straight connection, about one inch of additional clearance may be required behind the appliance if you’re trying to get it as close to a wall as possible. I have found replacement hoses with a right angle connection on Amazon, but I haven’t purchased one to confirm this gap could be eliminated.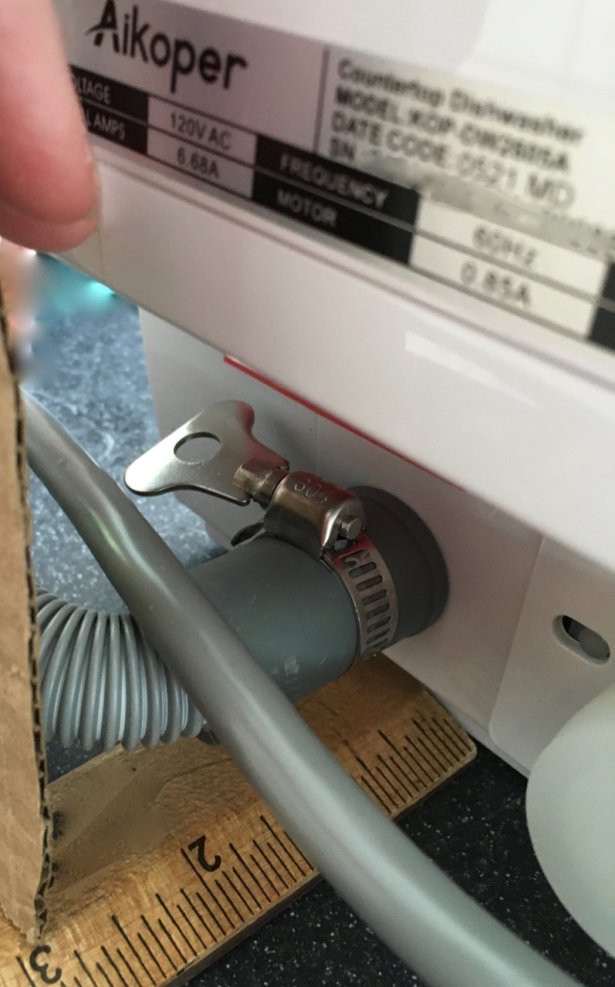
A small suction cup on the hose is supposed to keep its end inside your grey water bucket, but mine does not stay fixed to even the smoothest plastic waste container I’ve tried. Happily, the exiting water does not seem to flow with enough force to cause the hose fly around spraying filth, as was my initial fear.
Obviously, if you drain your dishwasher into a bucket, remember that you’ll need to lift the receptacle for emptying. With the machine’s approximately two gallon (6 L) capacity, expect a weight of about 15 lbs (6.8 kg) of grey water† to dispose of after running each load of dishes.
Those of us with arthritis or other physical limitations will benefit from emptying the waste bucket midway through a wash cycle. Doing so reduces the effort required vs. lifting a full bucket. I’m careful to keep a second, smaller dish handy to put the wastewater hose into while I do this, however, lest the machine discharge additional grey water at an inconvenient moment and flood my kitchen with filth!
 Most people probably have a sturdy office sized trash can, five gallon bucket, or other suitable container for catching wastewater in the quantity required. If looking to purchase a new, highly suitable receptacle, I’d suggest a Rubbermaid Commercial Crystal-Clear Square Storage Container in the 8 quart size which will accommodate more than 7.5 L, large enough to prevent splash-over messes.
Most people probably have a sturdy office sized trash can, five gallon bucket, or other suitable container for catching wastewater in the quantity required. If looking to purchase a new, highly suitable receptacle, I’d suggest a Rubbermaid Commercial Crystal-Clear Square Storage Container in the 8 quart size which will accommodate more than 7.5 L, large enough to prevent splash-over messes.
The 6 qt size pictured above in the same product line is sufficient to the task, but only just, and mine ended up perilously full when I used it without taking care to empty mid-cycle. You could make this container work for the task if you have one on hand, but I wouldn’t recommend its purchase for this particular job.
A bucket with a handle or handles will be easier to lift and empty.
A small, black rubber cap stoppered the drain port on the back of this dishwasher. In order to avoid losing this small piece, I used the tape that had been employed for security during its shipment to adhere the cap to the back side of my appliance. It will be useful to avoid inconvenient drips when moving the Aikoper immediately after use. Small amounts of water are likely to remain inside the machine for hours or days after the last cycle.
Dishwashers save water vs. hand washing
This seems like the right time to point out an easily overlooked fact: full size, modern (post-1994) dishwashers clean an entire load with about 5 gallons of water. Hand washing a sink full of dishes consumes more than five times as much—up to 27 gallons of fresh, potable water—while not offering any improvement in results.
The mini sized Aikoper Compact Portable uses just 1.6 gallons (6 L) per load though, to be fair, an overflowing double sink full of dirty dishes might take two cycles to get through.
Typically, dish-washing machines increase water temperatures to a sanitizing 140-150 °F, well above suggested water heater settings designed to protect children from scalding while saving energy.
The U.S. EPA recommends setting hot water heaters to 120 °F.
My new Aikoper Compact Portable dishwasher uses 162 °F for its hottest cycle, well above the temperatures at my tap. In 2021, even a little appliance such as this one includes an internal heating element to optimize wash and rinse temperatures and improve hygiene.
Growing up in the American West, I was taught to wash dishes using two basins for soapy and clear water; we never let the faucet run throughout the task! My family appears unable or unwilling to internalize these habits, so my search for a backup dishwasher has an altruistic motive as well as supporting my hatred for manual household chores.
Energy use—according to the Energy Guide yellow card standard with all American appliances for almost as long as I can remember—compares as favorably as one would expect between my broken-down Bosch and my new portable.
The U.S. Government suggests the Aikoper Compact Portable will consume 150 kWh/year of electricity.
Keep in mind that compact and full size dishwashers are not directly comparable using this system. Also, due to the years that passed between issuance of the Bosch label and today’s Aikoper label, average electricity rates grew from 8.28¢/kWh to 13¢/kWh whereas natural gas averages went from 65.6¢/therm to $1.05/therm in the same period.
My broken, full size Bosch was expected to consume 430 kWh/year vs. 150 kWh/year for the much smaller Aikoper. By comparison, the new, full size Miele I’ve ordered is rated at 230 kWh/year according to the manufacturer’s website.
Aikoper Compact Portable: Do dishes come out clean?
More than any other fact or feature about the Aikoper Compact Portable Dishwasher, what most want to know first is, “Will my dishes come out clean?”
“I always had to scrub or re-wash the spoons before. That doesn’t seem to be necessary with the new dishwasher.”